Difference Between https, http, www (All You Need To Know)
If you visit websites often you have probably noticed an https, http, or/and www at the start of the web address. But, what do they really mean, why do we need them and what are the differences between https,http and www?
Here is a table with all you need to know:
| https | http | www |
| Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer | Hypertext Transfer Protocol | WorldWide Web |
| More secure | Less Secure | Subdomain (such as maps.google.com, outlook.live.com) |
| Indicates How 2 Machines Will Communicate On the Web | Indicates How 2 Machines Will Communicate On the Web | It is Not Necessary For A Website |
| More Popular Nowadays | Less Popular Nowadays | Less Popular Than The Past |
Keep reading to find in detail what each term means.
http Explained
http is actually the language your web browser (ex chrome) and the server (a specialized type of computer) that stores your website use to communicate. The full name for http is Hypertext Transfer Protocol.
Web Browsers use http (or https) by default even if you type a domain name without it. So they already know that this is the proper language to communicate with a server. On the other hand, the server expects this kind of request.
This is how a request looks like: The browser wants to “GET” something from the server. In that case, since I typed “http://amazon.com”, the server responded that will redirect me to the “https://amazon.com”. That’s why we see the status code: 301 – Moved Permanently on the screenshot below.
The most usual status code is 200 (OK). In that case, the connection is successful and the server sends us the data we requested like the Html (code of the site), text, images, or videos.
If you are using chrome you can see how http works by pressing right click on your mouse > inspect > network and choose something from the name column.
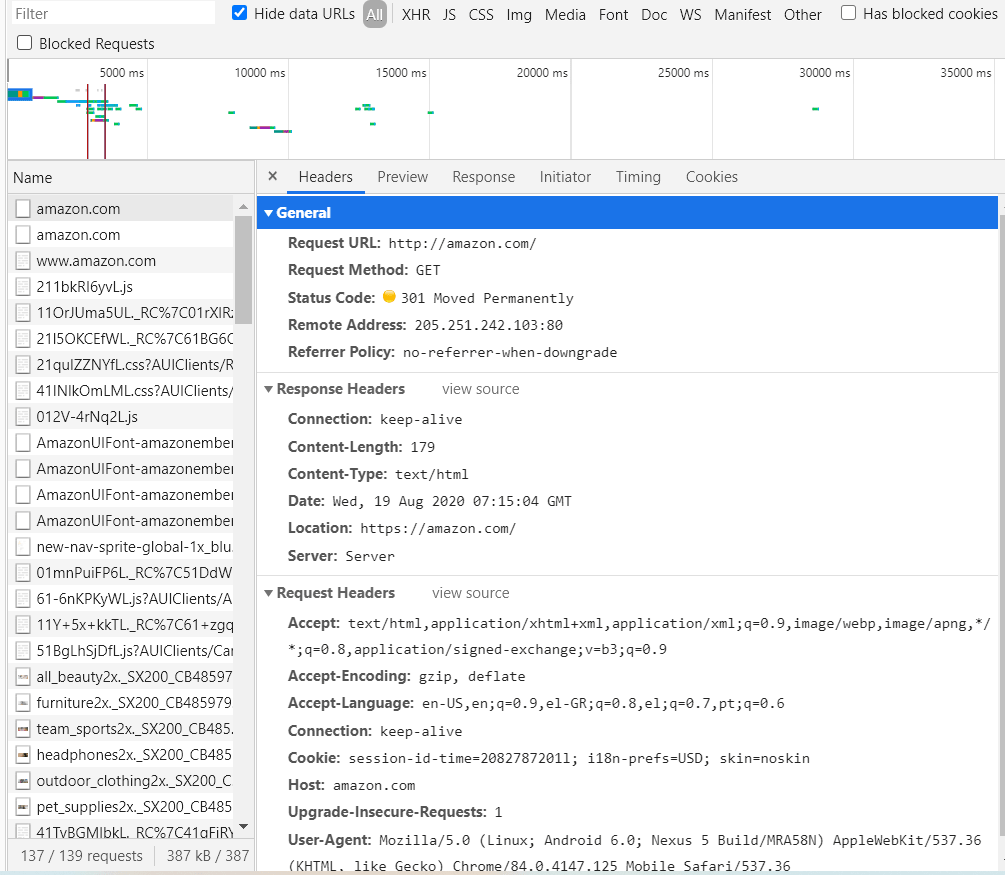
The downside with http protocol is that everything you and server exchange is visible to the public web so a hacker can see it easily. If you just browse a website it is not dangerous but if you send sensitive personal data such as a username, password or phone number then it is serious.
The “://” after http separates the protocol from the rest URL. Let’s present an example of a full URL so you can see how things work.
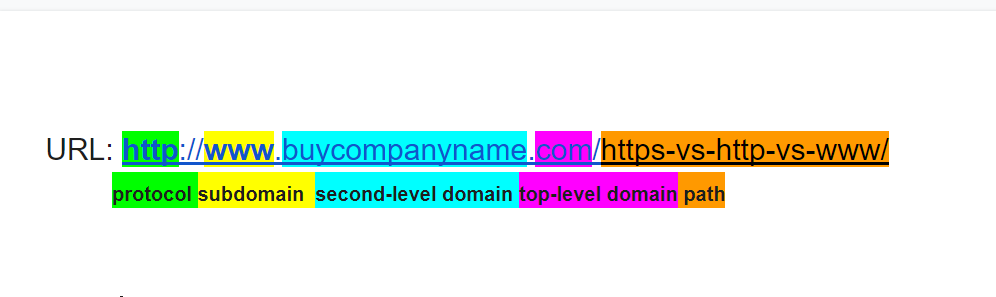
We already explained the http but your browser also needs to find where the server that stores the website is. The domain name (buycompanyname.com) is the human-readable version of an IP address (the specific address of the server). The subdomain is just a part of the domain and the path an even more specific address.
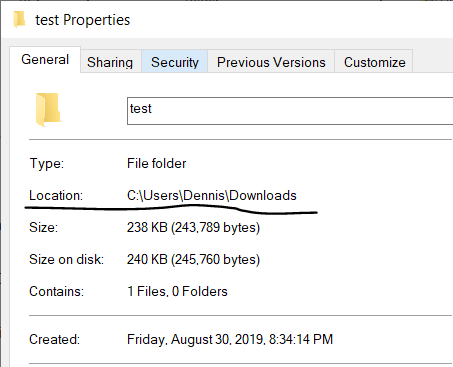
It is identical like when you searching a specific file on your pc. Choose a random file > right-click > General, You will see the exact location of this file. The same happens with a URL but on a bigger scale. You don’t search the location of a single file on your pc but instead the location (server) of a website on the public web.
There are many protocols such as http or https but we are not so used to seeing them. For example, ftp is used for transferring bigger files from a server and vice versa.
https Explained
https stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer and it is a more secure version of http. The big difference with http is that the data you exchange with a server is encrypted. Even if a hacker sees what you exchange with a site, he can’t read it. He will see just a random combination of characters and numbers. Only your browser and the server can decrypt those messages.
Here is how a https request looks like on the backend.
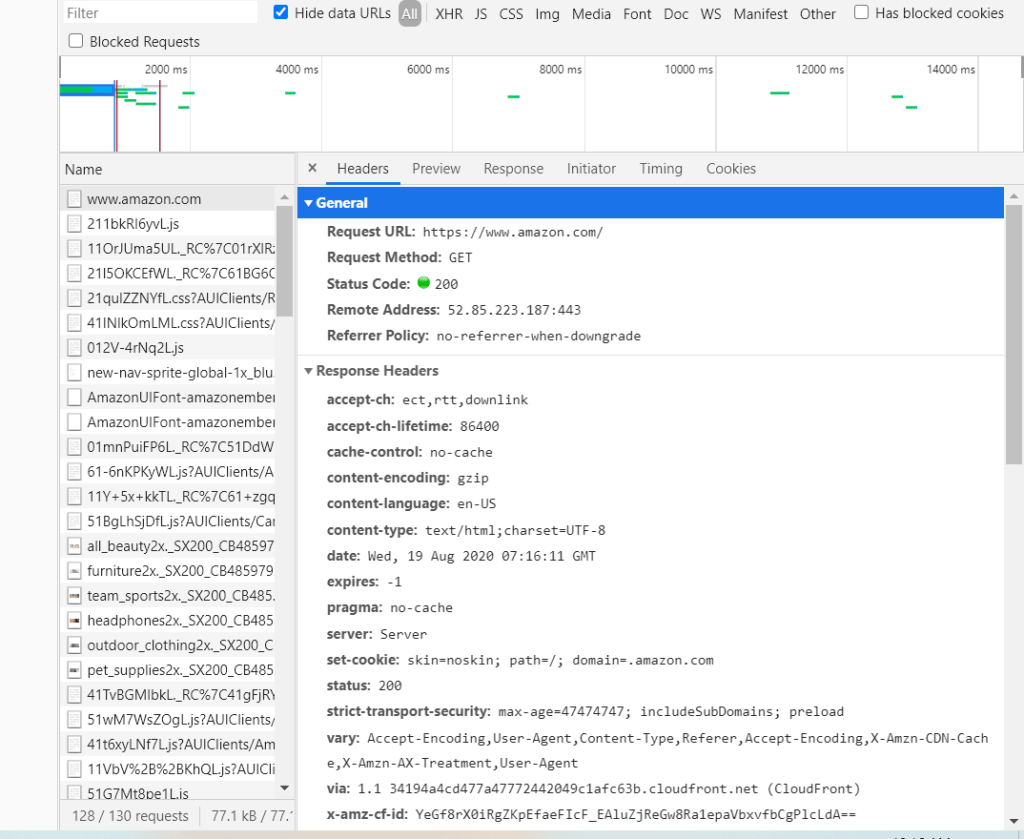
But how do we know if a website is actually secure? Website owners need to issue an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate from trusted sources. This certificate contains useful information such as the associated domain, owner details, the issuing authority, the issue date, the expiration date, etc.
If the certificate is valid, the browser and the website will start to exchange data.

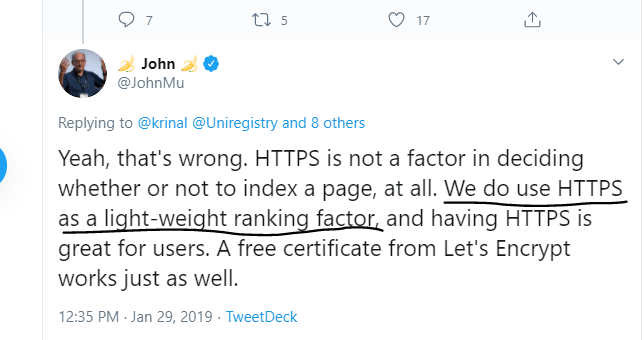
https protocol is superior for other reasons too. Search engines rank sites better if they use https instead of http even if they don’t collect sensitive data.
John Mueller is the Senior Webmaster Trends Analyst at Google and has confirmed that having a https is ranking factor. You can see here his tweet about this subject:
www Explained
www is just a subdomain like maps.google.com or login.yahoo.com. Websites use different subdomains to serve different purposes such as a login page or a specific service. The initials of www mean worldwide web and the usage of www comes from the early days of the internet.
In the beginning, the main usage of the internet was not for people to navigate on the public web. People were mainly exchanging emails and they were transferring files.
The www subdomain was an indication that people want to see the publicly available content of this domain. Nowadays when people visit a domain they want to see the public content by default. So, this habit is something that comes from the past.
Although big websites that use many subdomains for different services, they should use www because it makes sense since each subdomain has different usage. That’s why you see that all the big websites such as Facebook, Google, and Amazon use www for their public content.
**Tip: If you don’t see the https://www. in front of google, facebook or amazon just click twice on the URL on your browser. Chrome has decided to hide these details so you can see shorter urls.
Most website owners have set both www and non-www versions to redirect on the homepage. That helps search engines (like google) to understand that both versions represent the same page or else they will index 2 different versions of the site: one with www and one without.
Final Words
I hope the explanation was helpful and easy to understand. Please share the post on social media if you like it!